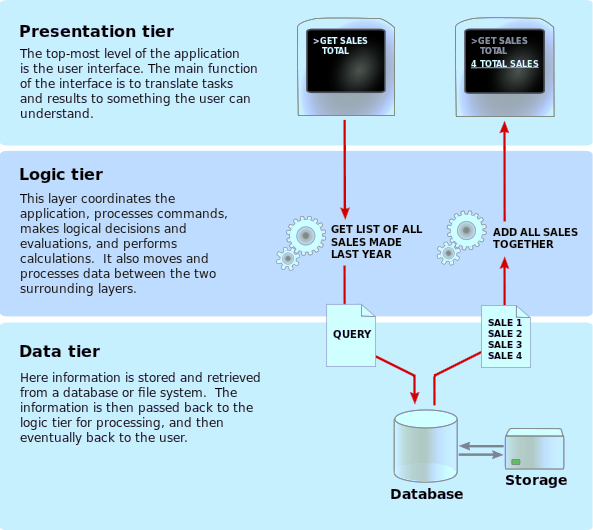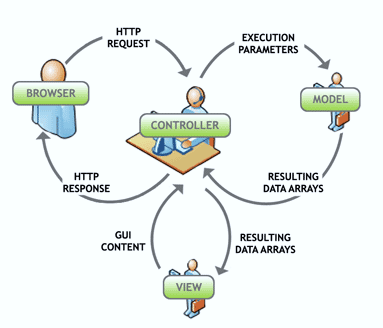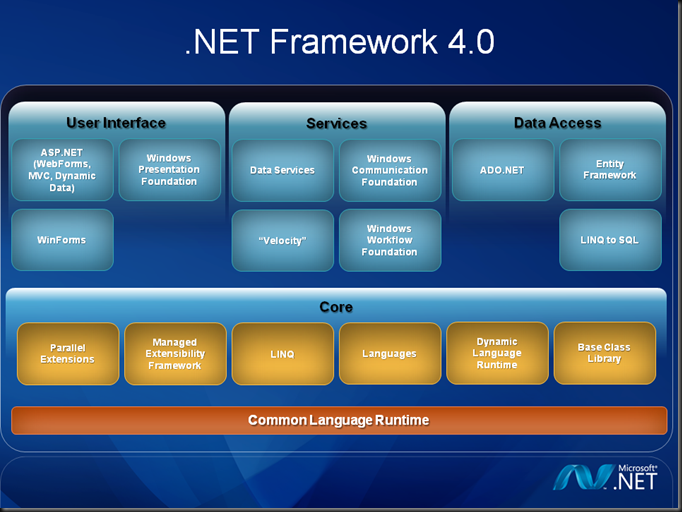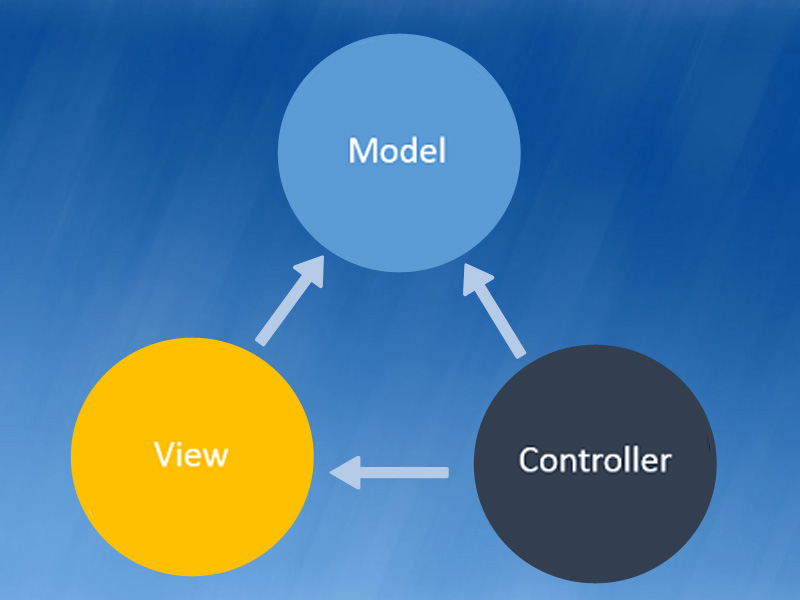
The Model-View-Controller (MVC) architectural pattern separates an application into three main components: the model, the view, and the controller. The ASP.NET MVC framework provides an alternative to the ASP.NET Web Forms pattern for creating Web applications. The ASP.NET MVC framework is a lightweight, highly testable presentation framework that (as with Web Forms-based applications) is integrated with existing ASP.NET features, such as master pages and membership-based authentication. The MVC framework is defined in the System.Web.Mvc assembly.
Overview {
MVC {
Concept and Origin;
Execution Process;
Popular Frameworks;
};
ASP.NET MVC {
MVC vs. Web Forms;
Features;
Music Store;
};
};
MVC Architecture Promotes:
- Code Reusability
- Shortens development
- Code Libraries
- Design Patterns
- Frameworks
- Separation of Concerns
- Improves code clarity and organization
- Helps troubleshooting by isolating issues
- Allows for multiple teams to develop simultaneously
- Controller – Mediates input and commands for the model or view
- Model – Application data, business rules, logic, and functions.
- View – Output and representation of data
Frameworks in different technology
- ASP.NET
- PHP (Zend, Symfony, CakePHP, CodeIgniter);
- Javascript ( Backbone.js, Ember.js, JavascriptMVC);
ASP.NET MVC
- Implements Model-View-Controller Paradigm
- Integrates with Existing ASP.NET Features
- Master Pages
- Membership-Based Authentication
MVC advantages over Web forms:
- Easier to Manage Complexity
- Does not use view state or server based forms
- Rich Routing Structure
- Support for Test-Driven Development
- Supports Large Teams Well
WebForms
- Preservers State over HTTP
- Page Controller Pattern
- View state or server based forms
- Works well for small teams
- Development is less complex
Models in MVC:
- Uses Entity Framework
- Database First
- Model First
- Code First
- Database Context
- Describes interactions between entities
- Data Annotations
- Describes additional requirements for the model
View in MVC:
- Razor
- Compact, Expressive, and Fluid
- Easy to Learn
- Has great Intellisense
- ASPX Engine
- Dynamic or Strongly Typed
- Partial Views
Controller in MVC:
- Requests routed to Controller::Action
- Action Methods
- Action Results
- Restful
Features of the ASP.NET MVC Framework
- Separation of application tasks (input logic, business logic, and UI logic), testability and test-driven development (TDD). All core contracts in the MVC framework are interface-based and can be tested by using mock objects, which are simulated objects that imitate the behavior of actual objects in the application. You can unit-test the application without having to run the controllers in an ASP.NET process, which makes unit testing fast and flexible. You can use any unit-testing framework that is compatible with the .NET Framework.
- An extensible and pluggable framework. The components of the ASP.NET MVC framework are designed so that they can be easily replaced or customized. You can plug in your own view engine, URL routing policy, action-method parameter serialization, and other components. The ASP.NET MVC framework also supports the use of Dependency Injection (DI) and Inversion of Control (IOC) container models. DI enables you to inject objects into a class, instead of relying on the class to create the object itself. IOC specifies that if an object requires another object, the first objects should get the second object from an outside source such as a configuration file. This makes testing easier.
- Extensive support for ASP.NET routing, which is a powerful URL-mapping component that lets you build applications that have comprehensible and searchable URLs. URLs do not have to include file-name extensions, and are designed to support URL naming patterns that work well for search engine optimization (SEO) and representational state transfer (REST) addressing.
- Support for using the markup in existing ASP.NET page (.aspx files), user control (.ascx files), and master page (.master files) markup files as view templates. You can use existing ASP.NET features with the ASP.NET MVC framework, such as nested master pages, in-line expressions (
<%= %>), declarative server controls, templates, data-binding, localization, and so on. - Support for existing ASP.NET features. ASP.NET MVC lets you use features such as forms authentication and Windows authentication, URL authorization, membership and roles, output and data caching, session and profile state management, health monitoring, the configuration system, and the provider architecture.